Silver
| General properties | |
|---|---|
| Name, symbol, number | silver, Ag, 47 |
| Element category | transition metal |
| Group, period, block | 11, 5, d |
| Standard atomic weight | 107.8682 |
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s1
2, 8, 18, 18, 1 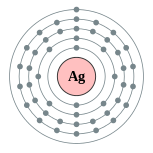 |
| Discovery | before 5000 BC |
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag (Greek: άργυρος<árgyros>, Latin: argentum, both from the Indo-European root *arg-for "grey" or "shining") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal. The metal occurs naturally in its pure, free form (native silver), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc refining.
Silver has long been valued as a precious metal, and is used as an investment, to make ornaments, jewelry, high-value tableware, utensils (hence the term silverware), and currency coins. Today, silver metal is also used in electrical contacts and conductors, in mirrors and in catalysis of chemical reactions. Its compounds are used in photographic film, and dilute silver nitrate solutions and other silver compounds are used as disinfectants and micro biocides (oligodynamic effect). While many medical antimicrobial uses of silver have been supplanted by antibiotics, further research into clinical potential continues.
Return to Periodic Table
No comments:
Post a Comment